What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A was first discovered vitamin, so named by the first letter of the Latin alphabet. It is especially important for maintaining good vision, good condition of the bones, skin, hair, teeth and gums. Without enough vitamin A, your body is prone to infections.
This vitamin is one of the most active antioxidants, and helps protect the skin from harmful sun rays. It is particularly important in the treatment of acne and fine wrinkles.
It has been proven that vitamin A acts prophylactically in some cancers, helps to reduce the level of bad cholesterol and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Vitamin A Deficiency Symptoms
Fortunately, most people get enough vitamin A through food. But the lack of this vitamin is rare though, it appears. Particularly at risk are people suffering from cancer, tuberculosis, pneumonia, chronic kidney disease or diseases of the prostate.
Some of the symptoms that occur when deficiency are:
- Affinity to viral infections
- Night blindness
- Hair loss
- Loss of appetite
- Problems with bones
- An overdose of vitamins A
Speaking of vitamin A will like, not to mention more about overdose with this vitamin. This phenomenon is called hypervitaminosis A and means that your body has stored more vitamin A than is necessary for proper operation.
Usually overdose vitamin A is obtained by excessive consumption of vitamin A as a dietary supplement. Hypervitaminosis A can lead to problems at birth, abnormal liver or problems with the central nervous system.
Some of the symptoms that occur during intoxication (hypervitaminosis) in vitamin A include loss of appetite, irritation, fatigue, brittle nails, headaches, vision problems, depression and anemia.
Receiving large amounts of vitamin A during pregnancy can cause miscarriage or defects in the newborn. Therefore, pregnant women should not receive vitamin A as a dietary supplement, unless recommended by a doctor.
Recommended daily vitamin A dosage
The recommended daily vitamin A needs vary depending on sex and age of the person.
- Children (3 years and younger) – 300μg
- Children (4-8 years) – 400μg
- Children (9-13 years) – 600μg
- Teens (14-18 years) – 900μg
- Adults (19 years and up) – 900μg
- Pregnant women (18 and down) – 750μg
- Pregnant women (18 and up) – 770μg
- Lactating women (18 and down) – 1 200μg
- Lactating women (18 and up) – 1 300μg
Due to the fact that there is a risk of toxicity (hypervitaminosis A) with vitamin A, given below are the maximum amounts of vitamin A, which can receive daily.
- Children (3 years and younger) – 600μg
- Children (4-8 years) – 900μg
- Children (9-13 years) – 1 700μg
- Teens (14-18 years) – 800μg 2
- Adults (19 years and up) – 3 000μg
- Pregnant or lactating women (18 and down) – 2 800μg
- Pregnant or lactating women (18 and up) – 3 000μg
Foods rich in vitamin A
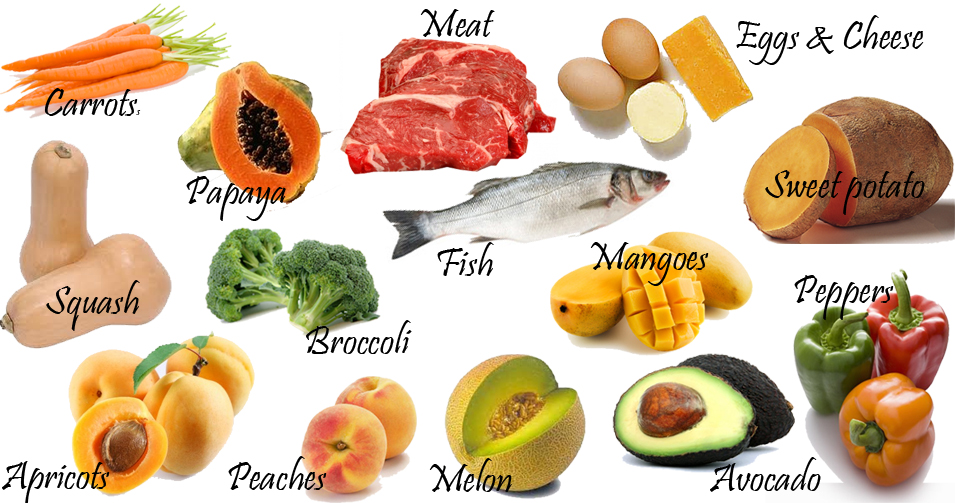
Foods rich in vitamin A
Vitamin A is present in fish oil, liver, eggs, milk and dairy products, tuna, dark green and yellow vegetables, carrots, cantaloupe, potatoes, etc..